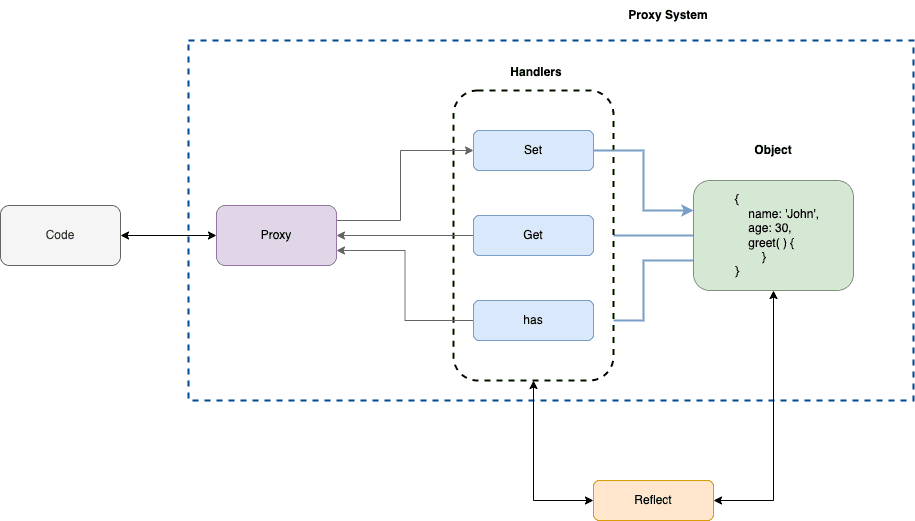
What is a JavaScript Proxy?
The Proxy object allows you to create an object that can be used in place of the original object, but which may redefine fundamental Object operations like getting, setting, and defining properties.
A few use cases are:
- Intercept property access: Intercept a field, log things, put analytics.
- Validation: You can validate each field before its value is set, throw errors if required.
- Format: You can format a field before its value is set.
- Infer: You can infer the value for a field from another field.
Overview
Tutorial on YouTube
Code Examples
Basic Syntax
const proxy = new Proxy(target, handlers);
Proxy without Handlers
const user = {name: 'John',age: 30,};const proxy = new Proxy(user, {});proxy.name = 'Mark'; // This will update the original user Objectconsole.log('Name: ', proxy.name);console.log('Age: ', proxy.age);
Output:
Name: MarkAge: 30
Get Handler
Use cases
- Retrieve a field value.
- Restrict access of a field value
Retrieve a value with log
const user = {name: 'John',age: 30,};const proxy = new Proxy(user, {get(target, prop) {console.log('Fetching from Proxy'); // Check this on console.return target[prop];},});proxy.name = 'Mark';console.log('Name: ', proxy.name);console.log('Age: ', proxy.age);
Access Restriction
const user = {name: 'John',age: 30,};const proxy = new Proxy(user, {get(target, prop) {if (prop === 'age') {console.error('[age] This field is not accessible publicly.');return 'NULL';}return target[prop];},});proxy.name = 'Mark';console.log('Name: ', proxy.name);console.log('Age: ', proxy.age);
Error:
Name: Mark[age] This field is not accessible publicly.Age: NULL
Set Handler
Use cases
- Correct, Format, and Infer a value before setting
- Validation
Age Validation
const user = {name: 'John',age: 30,};const proxy = new Proxy(user, {set(target, prop, value) {if (prop === 'age') {if (!Number.isInteger(value)) {throw new TypeError('The age is not an integer');}if (value > 150 || value < 0) {throw new RangeError('The age seems invalid');}}target[prop] = value;},});// SUCCESSproxy.age = 50;// ERRORSproxy.age = 200; // Uncaught RangeError: The age seems invalidproxy.age = -1; // Uncaught RangeError: The age seems invalidproxy.age = '30'; // Uncaught TypeError: The age is not an integer
Infer another field
const user = {name: 'John',age: 30,};const proxy = new Proxy(user, {set(target, prop, value) {if (prop === 'age') {target['isAdult'] = value >= 18;}target[prop] = value;},});// Yesproxy.age = 30;console.log(proxy);// Noproxy.age = 16;console.log(proxy);
Output
Proxy(Object) {name: 'John', isAdult: true, age: 30}Proxy(Object) {name: 'John', isAdult: false, age: 16}
JavaScript Reflect
Proxy and Reflect were both introduced in ES6 and are used for performing tasks, but they are a bit different.
Reflect is an inbuilt object that simplifies the creation of Proxy and makes it possible to call internal methods.
Simplify Proxy code with Reflect
const user = {};const proxy = new Proxy(user, {get(target, prop) {return Reflect.get(...arguments);},set(target, prop, value) {if (prop === 'age') {Reflect.set(target, 'isAdult', value >= 18);}return Reflect.set(...arguments);},});proxy.name = 'John';proxy.age = 30;console.log(proxy);proxy.age = 16;console.log(proxy);
Output
Proxy(Object) {name: 'John', isAdult: true, age: 30}Proxy(Object) {name: 'John', isAdult: false, age: 16}
Custom Solution: Build an Observer
Use Case
- We want to log the access of greet
- call logger.greetWillCall before greet and pass the arguments.
- call logger.greetDidCall after greet and pass the arguments.
Solution
const logger = {greetWillCall(args) {console.log('Greet will be called with arguments: ', args);},greetDidCall(args) {console.log('Greet Did be called with arguments: ', args);},};const user = {name: 'John',age: 30,greet(greetWith) {console.log(`${greetWith} ${this.name}`);},};const proxy = new Proxy(user, {get(target, prop, reciver) {switch (prop) {case 'greet':return function (...arg) {logger.greetWillCall(arg);const returnVa = target[prop].apply(target, arguments);logger.greetDidCall(arg);return returnVa;};default:return Reflect.get(...arguments);}},});// Greetproxy.greet('Hi!');
Output
Greet will be called with arguments: ['Hi!']Hi! JohnGreet Did be called with arguments: ['Hi!']
Summary
Thanks a lot for reading this article. If you liked it, or have any suggestions on feedback, please drop a comment on YouTube Video of this article.